
Contents
In the fast-changing world of business, where being innovative and adaptable is key to staying ahead, organizations are always on the lookout for ways to gain an edge over their competitors. One powerful tool that’s making a big impact is the 9-Box Grid. It might seem simple, but it’s changing how companies see, support, and make the most of their most important asset: their people.
Imagine walking into a room where you can see the future of your company laid out in front of you—not with complicated charts, but with a clear picture of everyone’s potential. That’s what the 9-Box Grid does. It goes beyond regular HR tools by showing us exactly where each person stands today and where they could go tomorrow, helping good companies become great and great companies become industry leaders.
This tool is not just about categorizing employees; it fosters strategic dialogues and informed decisions. Each quadrant of the grid—from top performers with high potential to underperformers with latent capabilities—presents opportunities for targeted interventions that align individual growth with organizational goals.
PwC’s CEO Survey provides compelling evidence for the urgent need for sophisticated talent management strategies. The survey found that 79% of CEOs are concerned about the availability of key skills, ranking it as one of the top threats to business growth. This concern has remained consistently high over the years, indicating a persistent challenge in talent management. But that’s not all!
55% of CEOs believe that the unavailability of key skills is impacting their ability to innovate effectively.
— PwC’s 27th Annual Global CEO Survey
This compelling data highlights the crucial connection between effective talent management and a company’s ability to innovate and expand. The 9-Box Grid represents a significant evolution in workforce assessment. In the past, organizations grappled with the dual challenge of identifying future leaders and optimizing current employee potential. Conventional performance evaluations often failed to capture the subtle attributes indicative of leadership potential, instead prioritizing short-term achievements. The 9-Box Grid addresses these limitations, offering a more comprehensive and forward-looking approach to talent assessment and development.
The 9-Box Grid addresses these challenges by integrating rigorous performance metrics with forward-looking potential assessments. It acts as a predictive tool, enabling organizations to foresee leadership gaps, nurture emerging talent, and cultivate a robust pipeline of capable successors. This approach not only enhances organizational resilience but also fosters a culture of continuous development and strategic alignment across all levels.
What is the 9-Box Grid?
The 9-Box Grid is a powerful tool frequently utilized by HR professionals and managers across various organizations. It serves as a matrix where employees are assessed based on two critical factors: their current performance and their potential for future growth within the company.
- Performance refers to how well an employee is currently executing their job responsibilities. This axis measures an employee’s current performance level in their role, typically assessed through performance reviews, KPIs, and feedback from supervisors.
- Potential, on the other hand, evaluates an employee’s capacity to take on more significant roles or responsibilities in the future. Factors influencing potential include skills, leadership qualities, adaptability, and career aspirations.
By plotting employees onto this grid based on their performance and potential, managers gain a clear visual representation of their workforce. This clarity aids in making informed decisions about talent development strategies, succession planning, and resource allocation. It helps identify high-potential employees who may benefit from additional training or career advancement opportunities.
Let’s dive deeper into the mechanics of this invaluable tool. The grid consists of nine boxes arranged in a 3×3 format. The horizontal axis typically represents an employee’s current performance, while the vertical axis measures their potential for future growth and advancement. This dual focus sets the 9-box grid apart from traditional performance evaluations, as it encourages leaders to consider not just what an employee is doing now, but what they might be capable of in the future.
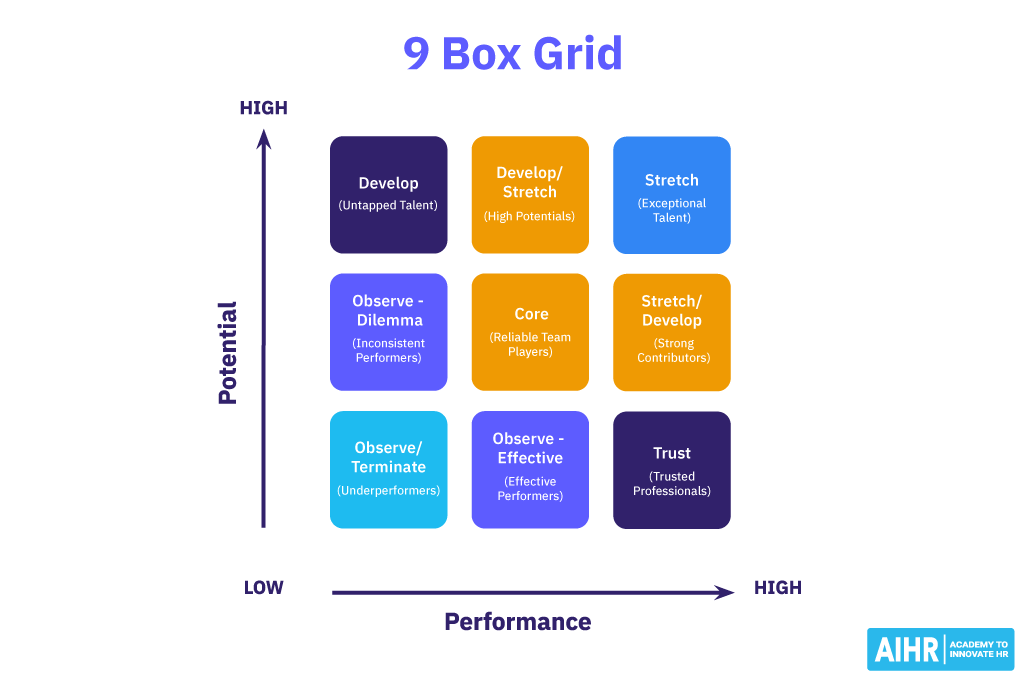
Each box within the grid represents a unique combination of performance and potential. For instance, the top-right box often represents high performers with high potential – your organization’s rising stars and future leaders. On the other end of the spectrum, the bottom-left box might indicate low performers with limited potential, signaling a need for intervention or reassignment.
The beauty of this structure lies in its flexibility and adaptability. Organizations can customize the criteria for each axis and the labels for each box to align with their specific culture, values, and strategic objectives. For instance, a rapidly growing tech startup might place a higher emphasis on potential and adaptability, while a more established corporation might weight current performance more heavily.
Moreover, the grid’s structure allows for nuanced discussions about employee development. It’s not just about identifying top performers or struggling employees; it’s about understanding the unique combination of performance and potential that each employee brings to the table. This nuanced approach enables more targeted development strategies and resource allocation.
The 9-Box Grid structure also facilitates comparative discussions. By plotting multiple employees on the same grid, organizations can gain insights into overall talent distribution, identify gaps in their talent pipeline, and make more informed decisions about succession planning and leadership development. It’s also crucial to remember that an employee’s position on the grid is not static. People can and do move between boxes as their performance improves or as they discover untapped potential. Regular reassessments ensure that the grid remains an accurate and useful tool for talent management.
Advantages of the 9-box Grid
The 9-box grid has gained significant traction in the world of talent management, and for good reason. This versatile tool offers a multitude of advantages that can transform how organizations approach their human capital. Let’s explore some of the key benefits that make the 9-box grid a valuable asset for businesses of all sizes and industries.
- Holistic Employee Assessment: One of the primary advantages of the 9-box grid is its ability to provide a more comprehensive view of an employee’s value to the organization. Unlike traditional performance evaluations that focus solely on past achievements, the 9-box grid combines current performance with future potential. This dual-axis approach allows managers to identify not just who’s performing well now, but who has the capacity to grow and take on greater responsibilities in the future.
- Strategic Talent Development: The 9-box grid serves as an excellent foundation for targeted employee development strategies. By clearly visualizing where each employee stands in terms of performance and potential, organizations can tailor their development initiatives more effectively. High-potential employees might be fast-tracked for leadership roles, while those with high performance but lower potential could be supported in becoming subject matter experts. This strategic approach ensures that development resources are allocated where they can have the most impact.
- Improved Succession Planning: A strong leadership pipeline is essential for organizational resilience and growth. The 9-box grid stands out as an exceptional succession planning tool, enabling companies to pinpoint and cultivate future leaders across all organizational tiers. By identifying high-potential talent early, organizations can strategically invest in targeted experiences and training, preparing these individuals to seamlessly step into pivotal roles when opportunities arise. This forward-thinking approach to succession planning not only mitigates risks associated with leadership transitions but also fosters a culture of continuous development and internal mobility. Ultimately, the 9-box grid empowers organizations to build a sustainable leadership ecosystem, ensuring continuity and driving long-term success in an ever-evolving business environment.
- Enhanced Talent Retention: When used transparently, the 9-box grid can be a powerful retention tool. Employees who see a clear path for growth and development within the organization are more likely to stay. The grid provides a framework for meaningful career conversations, allowing managers to discuss an employee’s current standing and future opportunities. This level of clarity and investment in employee growth can significantly boost engagement and loyalty.
- Resource Optimization: In a world of limited resources, the 9-box grid helps organizations allocate their talent management investments more efficiently. By clearly identifying different employee segments, companies can tailor their approaches. For instance, they might invest heavily in developing high-potential employees, while focusing on performance improvement for those in the lower quadrants. This targeted approach ensures that resources are used where they can generate the best returns.
- Risk Management: The 9-box grid can also serve as an early warning system for talent-related risks. It can help identify high-performing employees who may be at risk of burnout, or spot potential retention risks among top talent. This foresight allows organizations to take proactive measures to address these risks before they escalate into larger issues.
Implementing the 9-Box Grid:
The 9-Box Grid is a powerful tool for talent management, but its effectiveness hinges on proper implementation. A thoughtful, strategic approach to rolling out and maintaining this framework can transform it from a simple chart into a dynamic driver of organizational success. Let’s explore the key elements of successful 9-Box Grid implementation in depth.
- Define the Purpose and Scope
To begin, it’s crucial to define the purpose and scope of your 9 Box Grid implementation. Clearly articulate why you’re implementing this tool – whether it’s for succession planning, talent development, or overall workforce assessment. This foundational step will guide all subsequent decisions and ensure that the 9 Box Grid aligns with your organization’s strategic objectives.
- Clear Criteria:
At the heart of any successful 9-Box Grid implementation lies a set of clear, well-defined criteria for both performance and potential. These criteria serve as the compass guiding all evaluations, ensuring consistency across departments and reducing subjectivity in assessments. When establishing performance criteria, consider factors such as achievement of objectives and key results (OKRs), quality of work output, adherence to deadlines, contribution to team goals, and alignment with company values. For potential criteria, you might include leadership capabilities, learning agility, adaptability to change, (current or emerging), problem-solving skills, and career aspirations and drive.
Performance Criteria:
- High Performers: Consistently exceed expectations, deliver high-quality results, and contribute significantly to organizational goals.
- Moderate Performers: Meet expectations, deliver satisfactory results, and contribute to team goals.
- Low Performers: Do not meet expectations, require improvement, and may not consistently deliver required results.
Potential Criteria:
- High Potential: Shows capacity for leadership roles, demonstrates learning agility, and has the capability to grow within the organization.
- Moderate Potential: Has some potential for growth and development but may need more experience or training.
- Low Potential: May not have the ability or desire to take on higher responsibilities or leadership roles.
It’s crucial that these criteria are specific and measurable, avoiding vague terms in favor of concrete, observable behaviors or outcomes. They should be aligned with organizational goals, ensuring they reflect what truly matters for your company’s success. Clear communication of these criteria is essential; all stakeholders should understand what’s being measured and why. Collect relevant data on employee performance and potential. This can include performance reviews, 360-degree feedback, manager evaluations, and any other pertinent information. Lastly, consistent application is key. Train evaluators to interpret and apply the criteria uniformly across the organization.
- Place Employees in the Grid
Once the grid is set up, evaluate each employee according to the established criteria and place them in the appropriate box within the grid. The top-right box represents employees with both high performance and high potential—these are your star performers and future leaders. The middle-right box includes employees with high potential but moderate performance, indicating that while they have the capacity to grow, their current performance needs improvement. The bottom-right box is for high potential employees who are currently underperforming; they possess the ability but are not meeting expectations.
The top-middle box houses high performers with moderate potential, solid contributors who may not advance far in the hierarchy but are crucial for stability and performance. The center box is for moderate performers with moderate potential, representing steady contributors who may require some development to reach their full potential. The bottom-middle box contains employees with moderate potential but low performance, indicating a need for significant improvement.
The top-left box is for high performers with low potential, excellent in their current roles but not likely to advance significantly. The middle-left box is for moderate performers with low potential, consistent in their performance but with limited growth prospects. Finally, the bottom-left box is for low performers with low potential, often indicating a need for reassessment or transition strategies.
- Develop Action Plans
After categorizing employees, it’s essential to develop tailored action plans to address their specific needs and align their growth with organizational goals. For high performers with high potential, provide leadership opportunities, advanced training, and mentorship to prepare them for future roles. High performers with moderate potential should receive skills enhancement programs to help them maximize their capabilities.
For high performers with low potential, recognize their contributions and provide stability in their current roles. Moderate performers with high potential need investment in training and development to boost their performance. Moderate performers with moderate potential should receive regular feedback and development opportunities to ensure steady growth.
For moderate performers with low potential, monitor their performance and provide necessary support to maintain their current level. High potential but low-performing employees require identification of performance barriers and provision of coaching and support. Low performers with moderate potential need clear improvement goals and support to enhance their performance, while low performers with low potential may require reassessment and potential transition strategies if improvements are not seen.
- Regular Updates:
The 9-Box Grid is not a “set it and forget it” tool. To maintain its relevance and accuracy, regular updates are essential. These updates ensure that the grid reflects current realities and captures changes in employee performance and potential over time. Consider implementing formal reviews at least annually, ideally in conjunction with performance review cycles. However, don’t limit updates to these formal occasions. Encourage ongoing informal assessments throughout the year to capture real-time changes. Use project completions or significant milestones as triggers for reassessment. Implementing a system for managers to easily update their team members’ standings as needed can facilitate this ongoing process. Regular updates serve multiple purposes. They keep the grid accurate and current, enhancing its value for decision-making. They allow for tracking of employee development over time, providing insights into the effectiveness of development initiatives. Perhaps most importantly, they create opportunities for ongoing dialogue about performance and potential, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
- Collaboration:
Effective implementation of the 9-Box Grid requires collaboration across multiple levels of the organization. HR professionals, managers, and leadership must work together to ensure the grid aligns with organizational goals and is used consistently across the company. Cross-functional input on criteria development is crucial. Involve representatives from various departments to ensure the criteria are relevant across the organization. Calibration sessions bring managers together to discuss their assessments, ensuring consistency in how criteria are applied. Leadership involvement is key; engage top leadership in reviewing overall grid results and using insights for strategic planning. Throughout this process, HR should play a central role in managing the process, providing training, and ensuring fair application of the tool. This collaborative approach offers numerous benefits. It increases buy-in from all levels of the organization and leads to more accurate and fair assessments through multiple perspectives. It ensures alignment of talent management practices with overall business strategy and improves communication about talent across departments and hierarchical levels.
Final Thoughts
The 9 box grid’s strength lies not just in its simplicity, but in its capacity to spark meaningful conversations about talent development, succession planning, and strategic workforce alignment. By offering a clear visual representation of where employees stand and where they could potentially go, it enables organizations to make more informed decisions about resource allocation, development initiatives, and leadership pipelines.
However, it’s crucial to remember that the 9-box grid is not a magic solution, but rather a framework that requires thoughtful implementation and continuous refinement. Its effectiveness hinges on clear criteria, consistent application, and regular updates to reflect the dynamic nature of employee growth and organizational needs. When used effectively, the 9-box grid can transform how organizations approach talent management. It can help identify hidden gems within the workforce, provide targeted development opportunities, and ensure that high-potential employees are nurtured and retained.
Looking to enhance your talent management with a skills-focused approach? Discover how Nestor can transform your HR strategies. Contact us today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the 9-Box Grid?
The 9-Box Grid is a talent management tool used to evaluate and plot employees on a matrix based on two dimensions: their current performance and their potential for growth or advancement. This creates a 3×3 grid with nine boxes, each representing a different combination of performance and potential.
How does the 9-Box Matrix work?
The grid assesses employees on two axes: performance (typically on the x-axis) and potential (on the y-axis). Each axis is divided into three levels (low, moderate, high), creating nine boxes. Employees are then placed in the appropriate box based on their evaluated performance and potential.
Is the 9-Box Matrix only for large corporations?
While the 9-Box Grid is commonly used in large corporations, it can be adapted and used effectively by organizations of all sizes. The key is to tailor the criteria and implementation to fit the specific needs and culture of the organization.
What are the benefits of using a 9-box Matrix?
Key benefits include providing a visual representation of talent distribution, facilitating structured discussions about employee performance and potential, aiding in succession planning and leadership development, helping to identify skill gaps and development needs, assisting in resource allocation for employee development, and encouraging a holistic view of talent management.
How does the 9-box Matrix relate to other talent management tools?
The 9-box grid often complements other tools like performance reviews, competency frameworks, and individual development plans. It can provide additional context for these tools and help integrate various aspects of talent management.










