
Contents
Organizations depend on aligning workforce skills with strategic goals to achieve long-term success. A skills matrix is a structured tool that supports this alignment by mapping and analyzing employee competencies.
In this article, we’ll explore the crucial role and importance of skills matrices in modern organizations and explain the steps you need to take to reap the benefits of this dynamic tool. Let’s dive right in!
What is a Skills Matrix?
A skills matrix is a framework that enables HR and people managers to identify and visualize the skills and proficiency levels of employees in relation to their roles or the specific requirements of a given project.
You’ll encounter skills matrices in various easy-to-understand representations, which can be more complex or colorful, such as grids or charts, or as simple as a two-axis table.
The data parameters typically included in a skills matrix are:
- employee name and function
- skills and proficiency level(s)
- skill evaluation status

The Importance and Benefits of a Skills Matrix
Implementing a skills matrix can bring substantial advantages. It aligns competencies with organizational goals. Additionally, it enhances workforce retention and performance. Below are the core benefits.
1. Aligning Skills with Organizational Goals
A skills matrix effectively helps organizations match employee skills to business objectives. Consequently, it becomes easier to meet current and future needs. Furthermore, by mapping essential competencies for each role, companies can guide workforce development. This approach ultimately supports their mission. This approach provides employees with clarity about how their contributions impact the overall strategy.
2. Identifying and Retaining Top Talent
Managers can identify high performers and track their progress with the skills matrix, supporting career development and recognition. This clear visibility encourages talent retention. It shows employees a well-defined path for growth. It also helps management make data-driven decisions about promotions and targeted development.
3. Improving Resource Allocation Through Internal Mobility
A skills matrix reveals employees’ capabilities. Consequently, it allows leaders to assign roles and tasks to those best suited for them. With this insight, organizations can effectively place employees in positions where they can excel. As a result, this approach supports individual job satisfaction and enhances productivity. It also creates an optimized allocation of skills and resources.
Internal mobility is also key to retention: 67% of employees said they would quit their current job if their employer did not allow internal mobility, according to a Lever report. This shows the importance of aligning employees’ skills with the right roles.
4. Supporting Succession Planning
A skills matrix is essential for succession planning. It identifies employees with the right skills to fill key roles as they become available. This information allows organizations to prepare future leaders and ensure a seamless transition in critical positions.
Depending on the complexity of the job, it can take up to 1-2 years for a new hire to fully learn and excel in that role. This emphasizes the importance of proactive succession planning. Identifying potential leaders early enables targeted training to ensure their readiness.
5. Boosting Employee Engagement and Retention
A skills matrix provides employees with a clear development roadmap. By showing the skills needed to advance, the matrix fosters motivation and engagement. When employees see how their roles contribute to the organization and have opportunities for skill-building, they are more likely to remain committed and engaged in their roles.
This is particularly important considering that nearly half (46%) of employees say they are considering leaving their jobs in 2024—more than during the ‘Great Resignation.’ By utilizing a skills matrix, organizations can help employees visualize their growth potential and feel valued, ultimately reducing turnover and enhancing overall satisfaction.
6. Enhancing Recruitment and Onboarding
A skills matrix streamlines hiring by clarifying the skills and proficiencies required for each role. This allows hiring teams to select candidates who match the role’s specific needs. As a result, turnover is reduced. The onboarding process is also sped up. New employees adapt to their roles more quickly and confidently.
According to Test Gorilla’s State of Skills-Based Hiring 2024 report, 90 percent of respondents using skills-based hiring saw a reduction in mis-hires, and 91 percent reported improvements in retention. This data shows the effectiveness of aligning recruitment with clear skills requirements, leading to better job fits and longer employee tenure.
7. Identifying Skill Gaps and Development Needs
The matrix highlights gaps in employee competencies. Consequently, it helps organizations make informed decisions about training and hiring. Additionally, by regularly updating the skills matrix, companies can identify areas that need improvement. This proactive approach, therefore, allows them to address gaps effectively. As a result, the workforce remains competitive and capable.
The work and impact of L&D specialists in today’s work environment are crucial — especially since organizations already face a severe shortage of key talent, and 90 percent say they will have a meaningful skills gap in the coming years.
8. Designing Effective Training Programs
Using a skills matrix, organizations can create focused training programs to address actual needs, rather than offering generic sessions. Tailored training ensures that learning resources are directed at the skills most relevant to current roles, enhancing training impact and employee growth.
9. Supporting Performance Management and Career Development
A skills matrix provides a clear structure for performance evaluations by defining specific skills and competencies for each role. This framework guides managers in assessing employee progress objectively. It offers a foundation for career development discussions. This helps employees understand the skills they need to grow within the organization.
10. Building Balanced Teams
A skills matrix helps managers assemble teams with complementary skills. By understanding each team member’s strengths, leaders can create well-rounded teams. These teams can collaborate effectively, leveraging diverse skills. This approach leads to strong results and improved team performance.
When Should You Use a Skills Matrix?
A skills matrix proves useful in a variety of situations to maximize team and organizational effectiveness. Here are some scenarios where a skills matrix is especially valuable.
Assessing Team Skills for Projects
Before beginning a project, it’s essential to assess whether the team possesses the skills necessary for success. A skills matrix enables a quick assessment of current competencies. It compares these competencies against project requirements. This allows managers to make informed choices about additional training. It also helps in resource allocation.
Gaining Skills Visibility Across Teams
For a clear view of team competencies, a skills matrix is essential. It allows managers to quickly understand the skills within the team, simplifying task and project assignments. This visibility also supports collaboration, as team members can more easily identify others with complementary skills.
Optimizing Resource Allocation
Knowing which employees hold specific skills allows managers to assign tasks more effectively. This approach maximizes productivity and helps employees work in areas where they perform best, promoting both job satisfaction and overall efficiency.
Facilitating Talent Development and Training Needs
A skills matrix helps managers identify skill gaps and areas where training is needed, enabling targeted development initiatives. This ensures that training resources are directed toward competencies that benefit both individual career aspirations and organizational goals.
Supporting Succession Planning
For planned leadership transitions, a skills matrix identifies potential successors by comparing required skills for critical roles with those of current employees. This insight allows for strategic succession planning, creating a pool of capable leaders ready to step into key roles as needed.
How to Create a Skills Matrix
Step 1: Identify the Skills to Evaluate
Both soft and hard skills can be included in a skills matrix, as well as their sub-skills or sub-categories. It all depends on the scope and focus of the matrix and answering questions like:
- Do we address just a small team, a full department, or the entire organization?
- Is it more beneficial or impactful to create separate matrices for soft and hard skills?
- Given the importance of leadership skills, should we address them separately?
For this step, consider this:
- Outline Key Skills by Role Start by listing the core skills required for each role in the organization. Divide these into technical skills (e.g., programming, data analysis) and soft skills (e.g., communication, problem-solving). This breakdown helps capture the full scope of competencies needed for each role.
- Consult Team Leads for Input Gather input from department heads and managers, who can offer insight into essential skills specific to their teams. This input ensures the matrix captures what’s really needed for each role.
- Align Skills with Organizational Goals Ensure the skills you identify align with broader organizational objectives. For example, if the company is expanding its data analytics capabilities, prioritize related competencies.
To get a better idea, let’s look at how a skills matrix looks in Nestor:

In this example, the matrix is targeting an entire team and the focus is on the soft or human skills each individual requires to perform their role. You can easily notice the simplicity and power of using this type of visual representation.
Colors instantly reveal whether a particular skill is above (green) or under (orange) the recommended level for that position (the number in the top right of each square). The lack of these colors, as is the case for the first employee, indicates they haven’t yet gone through an assessment for that skill.
The summary on the right provides real-time insights into the gaps within the team and can act as the basis for future targeted training and development programs.
Step 2: Define Skills and Proficiency Levels
Once you know the skills you want to evaluate, the next step is to set clear, measurable proficiency levels. Defining these levels allows for consistent assessments and helps clarify where each employee stands in terms of skill mastery.
- Set Clear Proficiency Levels Establish a standard scale for proficiency, such as:
- Beginner: Basic understanding, needs supervision.
- Intermediate: Works independently with good knowledge.
- Advanced: Expert level, capable of leading or mentoring others.
- Create Descriptions for Each Level Providing clear examples or descriptions for each proficiency level helps ensure consistency in assessments. For instance, a “beginner” in project management might understand planning basics, while an “advanced” level could involve leading complex projects end-to-end.
- Consider Future Needs Think about the skills your organization may require in the future and include them as needed. Proactively identifying these skills can help with long-term planning and make your matrix more sustainable.
Once established, skills can then be listed in the individual profile of each worker:
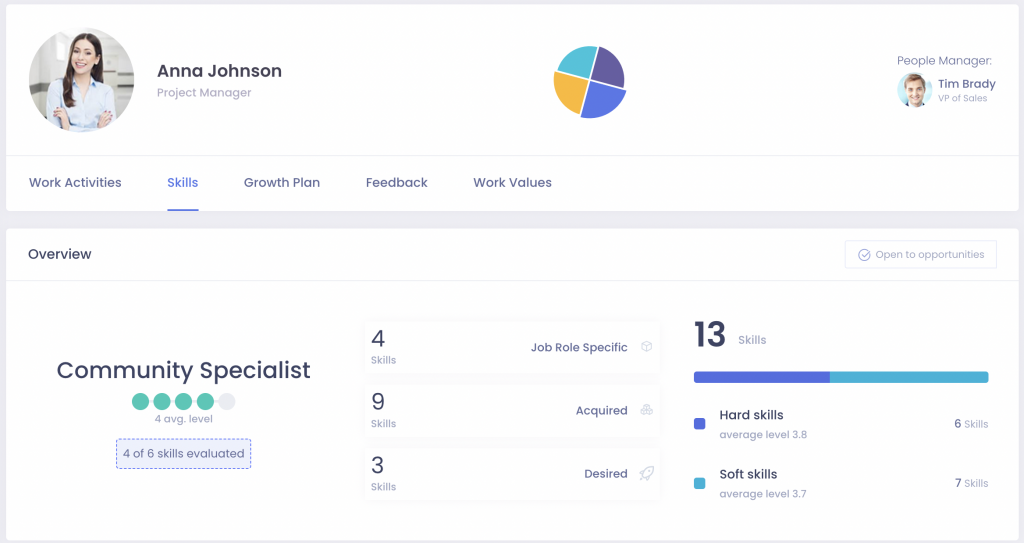
This profile highlights many useful skills data, including both job-specific skills as well as additional abilities that could reveal a particular employee is better suited for a different role or department.
It also highlights the average proficiency level for their skills and points out the competencies that haven’t been evaluated yet.
When it comes to proficiency, at Nestor, we use a 5-level skills grading system:
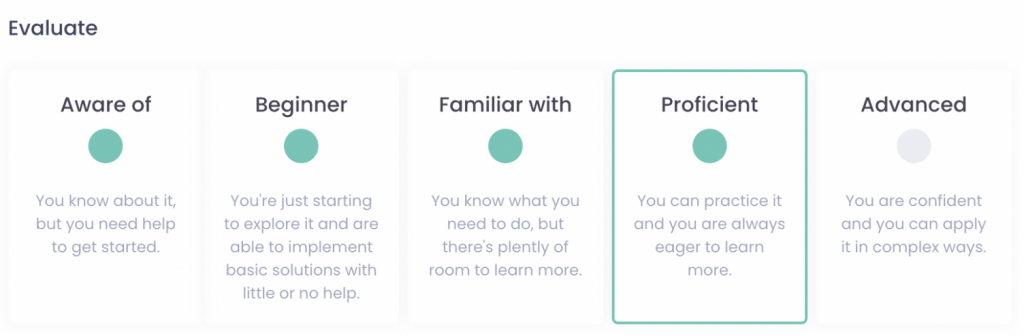
When defined clearly, these skills levels also help each employee understand where they currently stand and what they need to improve in order to perform better or become eligible for a career move, either vertically or laterally.
Step 3: Assessing the Skills of Your Employees
When it comes to skill assessment, a wide range of methods and tools are available. And combining them is what often provides the best and most accurate results.
Self-evaluations are important because they encourage employees to be more introspective and learn (or improve) how they assess their own abilities, traits, and work-related performance. This type of evaluation also has the potential to reveal skills that are either hidden or underused and lead to further discussions about exploring the full potential and skill set of that particular employee.
When conducted regularly and focused on skill development not only on productivity, performance reviews can also highlight the current status of an individual’s skill set and the potential for future growth. These review sessions also provide an opportunity to provide constructive feedback and choose the best training programs or learning materials to help the employee continue their development.
Peer or 360 feedback shouldn’t be overlooked either, since managers aren’t always the ones who interact the most with a particular worker. It’s often their peers who do that and who can observe over a period of time someone’s personal qualities and professional expertise.
Of course, companies can also use actual skill tests or simulations to evaluate proficiency levels. Valuable skills insights can also be extracted from training and development records, which show the actual learning outcomes of employees and their engagement in personal growth.
Step 4: Analyze and Implement Actions
The matrix is only as valuable as the actions it informs. This final step involves analyzing the data and using it to make strategic decisions on training, resource allocation, and internal mobility.
- Identify Skill Gaps Review the matrix to identify any critical skills that are lacking. This insight allows you to prioritize upskilling or hiring in areas that are most needed.
- Plan Development Programs Based on the identified skill gaps, create targeted training and development plans that address specific needs. Tailored programs are often more effective than one-size-fits-all approaches, leading to better outcomes.
- Support Internal Mobility Use the matrix to match employees with projects or roles that align with their skills and interests. This not only optimizes resource allocation but also enhances employee engagement by allowing them to work where they can thrive.
- Review and Update Regularly Keep the matrix relevant by updating it periodically to reflect changes in roles, skills, and organizational goals. Regular updates ensure that it remains a valuable tool for tracking growth and planning development initiatives.
Free Skills Matrix Template
To support your evaluation and development process, use our free skills matrix template. This template not only simplifies the assessment process but also tracks skills effectively. Consequently, it becomes easy to identify areas for growth and set actionable goals.
Simply map the necessary skills, define proficiency levels, and start tracking progress. Use this tool to enhance workforce planning, support internal mobility, and drive targeted skill development.
Challenges and Considerations
Creating a skills matrix brings specific challenges. Here’s a look at common issues and practical ways to address them:
Overcomplicating the Matrix
Skills matrices can quickly become too detailed. Extensive categories, skill levels, and descriptions can make the matrix hard to navigate. When it’s complex, employees may find it confusing, and managers may struggle to use it effectively.
Solution: Keep it simple. Focus on essential skills and limit proficiency levels to three or four (e.g., beginner, intermediate, advanced). Organize clearly, grouping related skills and using visual cues like color-coding. A streamlined matrix is easier for everyone to understand and use.
Subjective Skill Assessments
Assessing skills can be subjective, especially with self-assessments or single-manager evaluations. This can lead to inflated or underestimated ratings, reducing the accuracy of the matrix.
Solution: Use multiple perspectives. Combine self-assessments, peer reviews, and manager feedback. Standardize proficiency levels with clear criteria, such as specific tasks or examples for each level. This approach makes evaluations more balanced and objective.
Balancing Privacy and Transparency
A skills matrix reveals each employee’s strengths and areas for growth. While transparency can boost collaboration, it may also raise privacy concerns. Employees may worry about their skill levels being too visible, especially in weaker areas.
Solution: Protect privacy whenever possible. Additionally, limit matrix access to necessary personnel, such as HR and team leads. Moreover, communicate openly about how the matrix will be used. Emphasize its purpose for growth, not judgment. By respecting privacy, you build trust. As a result, you encourage participation.
Encouraging Employee Participation
For the matrix to work, employees need to be involved. However, some may see it as extra work without clear benefits. Lack of buy-in can lead to inaccurate assessments and lower engagement.
Solution: Involve employees early on. First, explain how the matrix helps identify growth opportunities and career progression. After that, allow employees to provide input on their assessments and desired skills. In addition, encourage open communication to foster trust. Moreover, regularly revisit the matrix to ensure it remains relevant. Ultimately, this approach engages employees and promotes their development.
Future Trends in Skills Matrices
The use of skills matrices is evolving with technology and changing workplace priorities. Here are some emerging trends:
- AI and Predictive Analytics: Advanced tools are enabling better skill mapping and predicting future talent needs.
- Integration with Learning Management Systems (LMS): Skills matrices are increasingly integrated with LMS to support continuous learning and development.
- Focus on Soft Skills and Hybrid Roles: As hybrid roles become common, soft skills are being prioritized alongside technical skills.
Final Thoughts
A skills matrix provides organizations with a structured approach to workforce management. Furthermore, it aligns employee skills with strategic goals. In addition, it identifies development needs and supports career growth. As a result, this approach fosters a productive and engaged workforce. Moreover, it enables companies to manage current resources effectively and prepare for future growth with confidence and clarity.










