Reinvention is a future of work trend that is already happening. It is no secret that generally, we live in much better conditions compared to the past. Our life as human beings improved a lot, which makes us looking for more meaning and growth opportunities everywhere. Hence, the future will continue to bring us more opportunities, changes and challenges.
This is why it is so important to be able to adapt and reinvent yourself. Reinvention means we will have to learn new skills, unlearn those that no longer serve us and re-learn other skills that will sustain us in the future.
Organizations’ role in this disruptive times
So how should organizations support employees in this reinvention process? And why should they do it? The more skillful and knowledgeable the workforce, the more innovative and profitable the company is. So now that we know why, let’s see how we can do it.
A significant part in reinvention is continuous development. Employee development and growth is a shared responsibility. Companies now are figuring out how to create proper upskilling and reskilling programs for their employees.
And neither the traditional training, nor the self-directed learning are fully covering the needs of the future-oriented employee. Subsequently, companies should focus on building capabilities, a set of skills, knowledge and experiences that employees need to be successful and thrive.
Moreover, these sets are extremely individual and unique for your company. So it is crucial to involve senior business leaders in their identification, constant update and full sponsorship. And this also refers to creating opportunities and assignments to practice what employees are learning and re-learning.
Reinvention through skills mapping and skills gap analysis
Hence we are experiencing this rapidly growing need for reskilling and upskilling, skills gap analysis becomes an extremely important tool. Shortly, a skill gap analysis helps identify the differences between the actual level of proficiency of a skill and the desired future one.
For a successful skills gap analysis, here are some steps you might consider looking into:
Skills mapping
Start with your company strategy. What are your strategic goals? Then, identify what are key-roles that impact those goals achievement? Next, make an inventory for each role and identify what will make an employee successful. In other words, define critical skills needs. Embrace the transition from role-based to a skill-based approach, being beneficial for many reasons.
For example, you might boost internal mobility. Having a clear picture of your colleagues’ skills you will be able to easily transition them into a new role. Another benefit of the skill-based approach is that during the recruitment processes, you will have a clearer picture of what skills the company already has and the ones it lacks.
Current skills assessment
Once identified and mapped the skills within your organization, assess their level of proficiency. Most probably, you already have a starting point: prior reviews (assessing skills and competencies) and lists of current qualifications and certifications your employees might have. Another cost-effective alternative is launching 360-degree reviews.
These reviews will allow you to have a much broader view by collecting different perspectives of the same skill for the same person. Alternative options for current skill assessment are observing your colleagues when they actually perform their job activities or testing their specific skills proficiency. Last but not least, of course, you can also draw upon an assessment center, for example.
Future and desired skills
Here’s where more complex research is needed. Based on your company’s strategic goals, mission and vision, as well as industry and future of work trends, identify what skills you should focus on developing today to stay relevant tomorrow. What’s the level of proficiency for each of those skills you need to succeed?
It’s impossible to know what will happen in the future. However, we do have voices and experts who are focusing their time and energy into researching and identifying some trends that might help us prepare for the future needs.
Companies without the tools to account for the value of skills and capabilities lack oversight of the depreciation or appreciation of one of their key intangible assets—the capabilities of their workforce. Without that oversight, setting the right investment strategy for reskilling and upskilling becomes a challenging feat.
— World Economic Forum, The Future of Jobs Report 2020
Close the gaps
Differences between the actual level of skills and desired one is the gap you might want to focus on analysing. And then closing.
Here are some strategies to help employees practicing and developing skills:
- Volunteering projects. Give time to your colleagues to volunteer for a cause they believe in. They can do it either within their community or projects you signed up for as part of your company social responsibility plan.
- Virtual reality (VR) simulations. It’s already happening. Employees can use their mobile phones or any other devices to develop skills (for example, communication, conflict resolution, presentation, customer service training) by interacting with an avatar. VR simulations are also cost and time saving, compared to traditional training soft skills options.
- Gigs. There are companies that encourage their employees to take on other internal projects, aside from their daily job responsibilities. Or, in this modern world, gigs. These internal projects encourage your employees to continuously grow, try new things, acquire and develop new skills. Additionally to that, internal gigs also help your company achieve more and identify new talents.
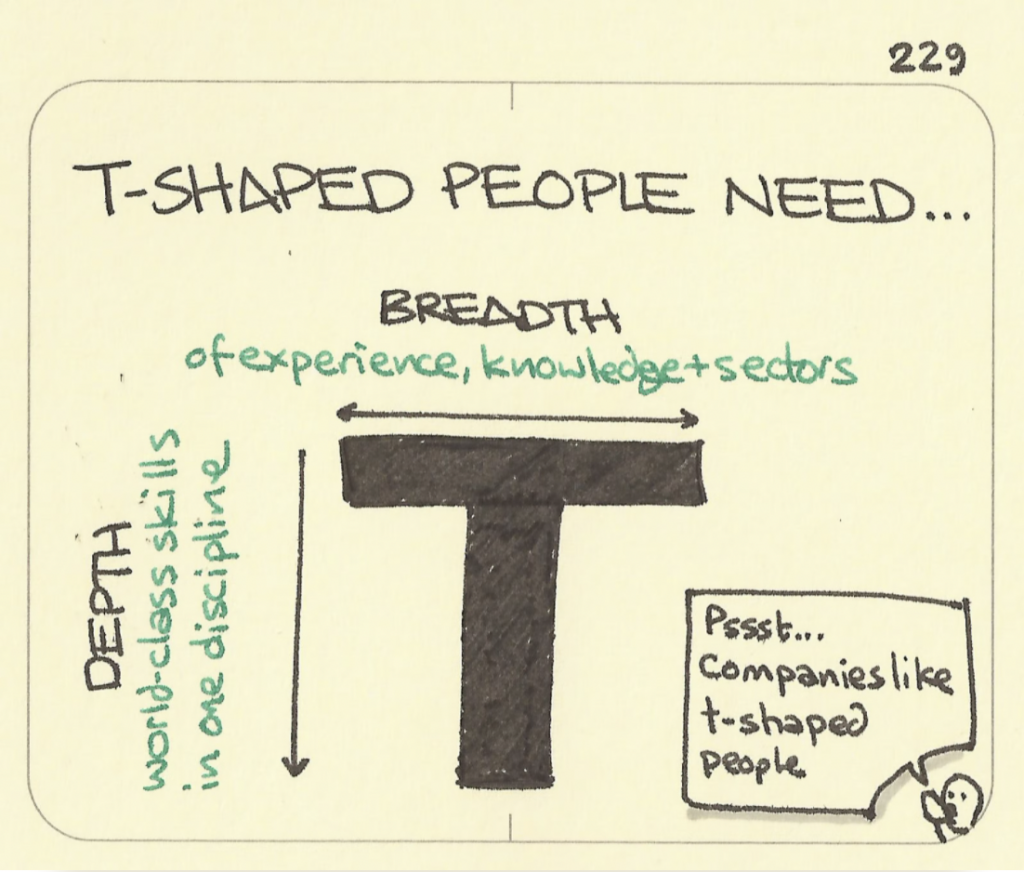
Will you reinvent your workforce into T-shaped professionals?
T-shaped professionals are people who need breadth of experiences, knowledge and industries, and depth of world-class skills in at least one discipline. In other words, guide your employees to become generalists in four core competencies and specialist in at least one functional competency.
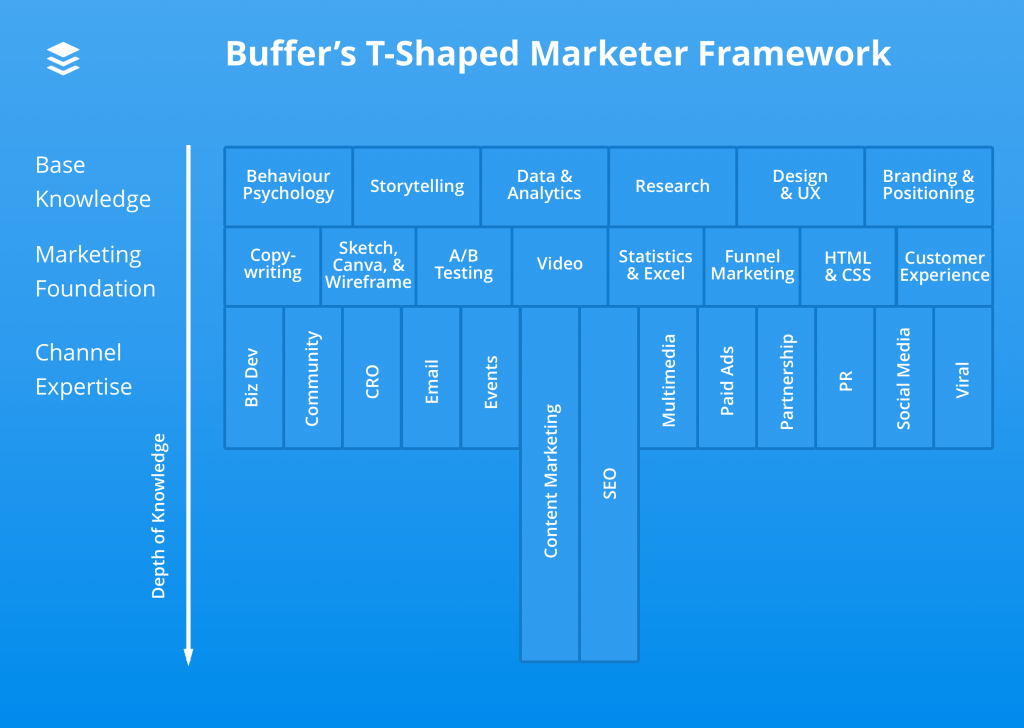
For a more practical example, let’s look into the T-shaped Marketer at Buffer.
A T-shaped Marketer at Buffer has the following skill set:
- base experience and knowledge in non-marketing areas, such as: behavioural psychology, analytics, research, branding, storytelling etc.,
- marketing foundation, and
- channel expertise (audience and acquisition channels): SEO, content marketing, events, business development etc.
With such a skills set a Marketer will be able to come up with innovative ideas and initiatives, while being relevant in the labor market. In conclusion, is continuous employees’ reinvention through upskilling and reskilling on top of your priority list?
Final notes
According to the World Economic Forum “Building a Common Language for Skills at Work A Global Taxonomy” Report, 50% of all employees will require reskilling by 2025 and 40% current workers’ core skills are expected to change by 2025. It is not an easy process. However, thankfully we leave the times when HR technology comes with a variety of incredibly useful tools to assist you.
However, it is a crucial step you might choose to start developing today to become future-ready. Simultaneously, focusing today on building a culture of upskilling and reskilling will positively impact your future recruitment and employee engagement budgets and people strategy overall.










