Contents
Data. It’s everywhere, shaping the way we work, shop, and even think. But when it comes to managing people, many companies still rely on gut instinct or outdated methods. Does that sound like your organization? If so, it’s time for a change. How? With HR Analytics, a powerful, data-driven approach that leverages advanced metrics, predictive insights, and AI to revolutionize how organizations understand, optimize, and empower their most valuable asset: people.
What if you could predict which employees are likely to leave? Or identify the perfect candidate before they even walk through the door? HR Analytics turns these scenarios into reality, shifting HR from a reactive function to a strategic driver of success.
But let’s be honest, many organizations are still figuring this out. Maybe your team is collecting data but doesn’t know what to do with it. Maybe you’re using spreadsheets when you need advanced tools. Or maybe the idea of “HR Analytics” feels too complicated to even start.
This guide is here to change that. We’ll break down what HR Analytics is, why it matters, and how you can use it to tackle everything from hiring to retention to performance. By the end, you’ll not only understand HR Analytics—you’ll know how to make it work for your organization.
What is HR Analytics?
A Simple Definition
HR Analytics is the process of using data to improve human resource decisions. It’s about collecting, analyzing, and interpreting workforce data to answer key questions:
- Why are employees leaving?
- What drives high performance?
- How can we predict future workforce needs?
While traditional HR metrics focus on basic reporting (e.g., ‘Our turnover rate is 15%’), HR Analytics uncovers patterns, predicts trends, and recommends actions.
A Brief History
Organizations didn’t develop HR Analytics overnight. Decades ago, companies began tracking metrics like headcount and payroll. The rise of big data and advanced analytics tools then transformed HR Analytics into a game-changer.
Leading companies like Google and Microsoft pioneered People Analytics, using data to make smarter hiring, retention, and performance decisions. Fast forward to today, and the combination of big data, artificial intelligence, and advanced analytics has given rise to Data-Driven HR.
Why HR Analytics Matters
HR Analytics isn’t just a trend; it’s something essential for modern organizations. According to SHRM Research, 94% of business leaders agree that People Analytics elevates the HR profession, showing its growing importance in driving business success. Additionally, 71% of HR executives who use People Analytics say it’s crucial to their organization’s HR strategy.
Here’s why HR Analytics matters:
- Improved Decision Making: Data-driven insights help HR professionals make smarter, more objective decisions.
- Enhanced Employee Experience: By understanding employee behavior, HR can tailor policies and initiatives that improve satisfaction.
- Higher Retention Rates: Predictive analytics helps identify retention risks, allowing organizations to act before losing talent.
- Optimized Performance: Analyzing performance data helps identify high-potential employees and provides targeted growth strategies.
In short, HR Analytics empowers HR teams to move beyond gut feeling and make evidence-based decisions that align with organizational goals.
HR Analytics in Skills-Based Talent Management
As organizations increasingly shift toward skills-based talent management, HR Analytics becomes a critical enabler. By leveraging analytics to understand employees’ skills, gaps, and future potential, HR teams can better align talent strategies with business needs.
Here’s how HR Analytics supports skills-based talent management:
- Identifying Skill Gaps: Advanced analytics tools pinpoint current and future skill deficiencies, allowing organizations to proactively train or hire talent.
- Personalized Development Plans: Insights from HR data enable tailored upskilling and reskilling programs, ensuring employees grow in areas most valuable to the organization.
- Strategic Workforce Planning: Analytics provides a clear picture of the skills available versus those required, helping HR teams design effective hiring and development strategies.
- Data-Driven Internal Mobility: Understanding employees’ skill sets through analytics promotes equitable and efficient internal hiring and career advancement.
By integrating HR Analytics into skills-based talent management, organizations can create a more agile, future-ready workforce. This foundation ensures that the right skills are in the right places to drive innovation and business success.
What are the four types of HR Analytics?
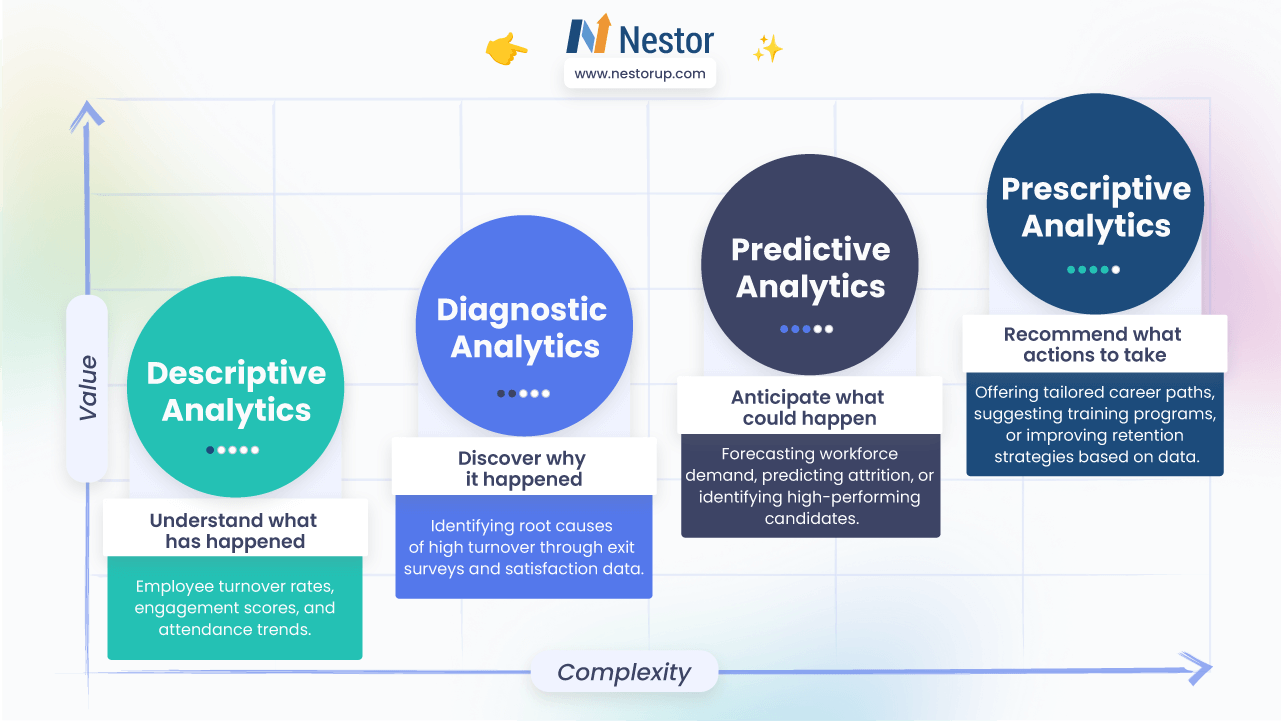
To understand how HR Analytics works, it’s important to recognize its main categories. The four main types of HR Analytics are:
1. Descriptive HR Analytics: Understanding Past Trends
Descriptive Analytics examines historical data to identify trends, patterns, and outcomes. It answers the question: What happened? In talent management, this analysis provides a foundation for understanding workforce performance, skill gaps, and development opportunities.
- What it does: Descriptive Analytics highlights past trends, such as skill proficiency levels, training completion rates, or internal mobility patterns. It helps HR teams identify areas where talent initiatives are succeeding or falling short.
- How it helps: While it doesn’t predict the future, Descriptive Analytics allows organizations to set benchmarks and diagnose issues. For example, analyzing performance reviews can reveal which skills consistently contribute to high performance.
- Example in practice: A tech company uses Descriptive Analytics to evaluate skill assessments across its engineering teams. The analysis reveals that advanced data science skills are lagging in certain teams. Leadership introduces targeted training programs to bridge the skill gap.
In fact, roughly two-thirds of organizations (68%) actively leverage descriptive analytics, recognizing its role in uncovering valuable workforce insights to guide future strategies.
2. Predictive Analytics: Forecasting Future Outcomes
Predictive Analytics uses historical talent data to forecast future trends and outcomes. It answers questions like: What is likely to happen?
- What it does: Predictive Analytics identifies patterns in workforce data to anticipate skills gaps, flight risks, or leadership pipeline shortages. It helps HR teams move from reactive to proactive talent management strategies.
- How it helps: By predicting outcomes, HR teams can prepare for talent challenges. For example, predictive models may show that employees with outdated skills are more likely to leave, prompting organizations to invest in upskilling initiatives.
- Example in practice: A global consulting firm analyzes learning and engagement data to predict which high-potential employees are likely to leave due to a lack of career growth opportunities. Armed with this insight, they implement tailored development plans, reducing attrition among key talent by 20%.
3. Prescriptive Analytics: Recommending Data-Driven Actions.
Prescriptive Analytics builds on predictive insights by recommending specific actions to improve talent outcomes. It answers the question: What should we do?
- What it does: This analysis provides data-driven solutions to talent management challenges. It helps HR teams determine the best strategies for upskilling, internal mobility, or leadership development.
- How it helps: Prescriptive Analytics identifies actionable steps for talent optimization. For example, it may recommend personalized learning paths to close critical skills gaps or suggest strategies to improve employee retention.
- Example in practice: A financial services company identifies a growing need for digital transformation skills. Prescriptive Analytics recommends an upskilling program focused on AI and machine learning for mid-level managers. After implementing the program, the company sees a measurable improvement in workforce readiness and innovation.
4. Diagnostic Analytics: Uncovering the Root Causes of HR Challenges.
Diagnostic Analytics uncovers the root causes behind talent management challenges. It answers the question: Why did this happen?
- What it does: By analyzing talent data in detail, Diagnostic Analytics identifies the factors driving issues like skills mismatches, low engagement, or leadership gaps. It reveals why certain teams or individuals struggle to meet performance goals.
- How it helps: Instead of guessing why a workforce problem exists, HR teams gain clear insights. This enables organizations to address challenges effectively and ensure talent strategies align with business needs.
- Example in practice: A healthcare organization struggles with low productivity in its nursing staff. Diagnostic Analytics reveals that nurses lack access to necessary skill development programs. In response, the organization introduces targeted clinical training, leading to improved patient care outcomes and staff satisfaction.
How These Types Work Together
Each type of talent management HR Analytics plays a crucial role, but their power multiplies when combined. Think of them as building blocks for a comprehensive talent strategy:
- Start with Descriptive Analytics to identify current skill gaps, workforce trends, and performance benchmarks.
- Use Predictive Analytics to anticipate future talent needs, skills shortages, or turnover risks.
- Apply Diagnostic Analytics to uncover the reasons behind talent challenges, such as low engagement or stagnant career growth.
- Leverage Prescriptive Analytics to implement solutions, like upskilling programs, succession planning, or targeted engagement initiatives.
Example in practice: Imagine an organization struggling to fill critical leadership positions:
- Descriptive: Analyze current data to understand which teams have the largest leadership gaps.
- Predictive: Forecast future leadership shortages based on retirement trends and performance metrics.
- Diagnostic: Identify why internal candidates are not ready—whether it’s a lack of training or career pathways.
- Prescriptive: Introduce leadership development programs and personalized coaching to build a strong leadership pipeline.
By combining all four types of analytics, HR teams can make evidence-based decisions that align talent strategies with organizational goals. Talent management becomes proactive, data-driven, and focused on continuous growth.
Key Applications of HR Analytics in Skills-Based Talent Management
HR Analytics plays a critical role in skills-based talent management by helping organizations identify, track, and optimize their workforce’s skills. From driving employee engagement to addressing skills gaps and aligning performance with business goals, HR Analytics enables organizations to build a future-ready workforce.
Skills-Based Employee Engagement and Retention
Engaged employees are more likely to stay and contribute meaningfully to an organization, especially when they see opportunities for growth and skills development. HR Analytics provides actionable insights to foster engagement and reduce turnover.
- Understanding Skills Engagement Trends: By analyzing engagement surveys, sentiment data, and skills usage, HR teams can uncover patterns that impact employee morale. For example, employees in roles where skills are underutilized may experience frustration or disengagement. HR Analytics helps identify these trends and address them by aligning employees with projects or roles that match their skills.
- Identifying Retention Risks: Predictive analytics helps flag employees at risk of leaving due to skills stagnation, limited growth opportunities, or a lack of clear career progression. With these insights, organizations can offer targeted learning and internal mobility programs to keep employees engaged and motivated.
- Promoting a Culture of Continuous Skills Development: HR Analytics measures the effectiveness of learning and development initiatives, such as upskilling programs or skills-based mentorship. This ensures that employees see a clear path to growth and remain engaged while contributing their skills to organizational success.
Skills-Driven Performance Management
Performance management becomes more impactful when it focuses on developing and leveraging employees’ skills. HR Analytics transforms this process with data-driven insights that help assess performance objectively, identify high-potential talent, and address skill gaps.
- Linking Skills to Performance Outcomes: HR Analytics connects skills data to business outcomes, enabling organizations to understand which skills directly impact productivity, team performance, or project success. For example, analytics might show that proficiency in certain technical skills drives faster project completion rates.
- Identifying High-Potential Talent: By analyzing performance metrics, skills assessments, and peer reviews, HR teams can pinpoint employees with high-growth potential and essential skills. These insights enable targeted development efforts to nurture emerging leaders and top performers.
- Customizing Skills Development Plans: Analytics identifies skill gaps on an individual and team level, allowing managers to create personalized development plans. Whether it’s upskilling for new tools or reskilling for evolving roles, these insights ensure employees are equipped to excel.
Skills-Focused Workforce Planning
Strategic workforce planning ensures the organization has the right skills in the right roles to meet current and future business demands. HR Analytics provides clarity and precision for skills-based planning.
- Identifying Skills Gaps: By analyzing workforce skills data, organizations can identify current shortages and forecast future skill gaps. For example, trends might reveal that a team lacks proficiency in emerging technologies, prompting targeted reskilling initiatives.
- Optimizing Skills Distribution: HR Analytics helps organizations allocate talent effectively by aligning employees’ skills with critical projects or departments. This ensures that the right skills are utilized where they can drive the greatest impact.
- Anticipating Future Skills Needs: Predictive analytics enables organizations to anticipate evolving skill demands caused by technology shifts, business growth, or industry changes. By planning proactively, HR teams can implement upskilling and reskilling programs to future-proof their workforce.
Enhancing Learning and Development (L&D)
A skills-based approach to talent management requires continuous learning and growth. HR Analytics ensures learning programs are data-driven, targeted, and impactful.
- Aligning L&D with Skills Needs: HR Analytics identifies the skills employees need to succeed in their roles and highlights gaps that require attention. This enables HR teams to design training programs that are aligned with both individual career paths and organizational goals.
- Measuring L&D Effectiveness: Analytics evaluates the impact of learning initiatives by tracking skills progress and performance outcomes. For example, HR teams can measure how upskilling programs improve productivity, team efficiency, or employee satisfaction.
- Facilitating Career Mobility: By tracking employees’ skills development over time, HR Analytics helps identify opportunities for internal mobility. Whether through lateral moves, promotions, or new role assignments, organizations can align career paths with skills growth, keeping employees motivated and engaged.
Why Skills-Based HR Analytics Matters
HR Analytics transforms talent management by shifting the focus to skills as the foundation for workforce success. It enables organizations to:
- Identify and close skills gaps to drive productivity and innovation.
- Foster employee engagement through targeted development and growth opportunities.
- Optimize workforce planning to ensure the right skills are in the right place at the right time.
- Support continuous learning to build an agile, future-ready workforce.
By leveraging HR Analytics, organizations can align employee skills with strategic goals, create a culture of growth, and ensure teams are equipped to meet evolving challenges.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of HR Analytics in Action
Google’s Use of Analytics
Google uses People Analytics to improve HR processes and make smarter decisions. Instead of relying on traditional hiring methods, Google looks at data from past hires to understand what makes employees successful. This helps them focus on qualities like cognitive ability and cultural fit, ensuring they hire the right people.
For employee engagement, Google regularly surveys staff and reviews exit interviews to spot trends. When work-life balance became a concern, they introduced flexible hours and extra vacation time. This proactive approach helps retain employees and keeps them happy.
Google also uses data to improve performance. Through Project Oxygen, they identified key traits of great managers, like coaching skills and emotional intelligence. This insight led to better manager training and higher employee satisfaction.
In short, Google’s use of People Analytics has helped them make better HR decisions, improve employee experience, and build a more inclusive work environment.
eBay’s Use of Analytics
eBay uses People Analytics to transform its HR processes and improve decision-making. They focus on using data to better understand employee needs, drive performance, and enhance retention. By analyzing employee data, eBay is able to identify the key drivers behind employee engagement and satisfaction.
One major area where eBay has applied People Analytics is in improving leadership. The company uses data to assess management performance and identify areas for improvement. This approach helps them provide targeted leadership development, ensuring that their managers are equipped to support and engage their teams effectively.
eBay also uses analytics to monitor and improve employee retention. By tracking key factors like job satisfaction and career development, they can identify potential issues early on and take action to prevent turnover. This proactive approach helps eBay retain top talent and keep employees engaged.
In summary, eBay’s use of People Analytics has allowed them to make smarter HR decisions, enhance employee engagement, and build a stronger, more effective workforce.
NASA Use of Analytics
NASA is changing its HR approach by using People Analytics to make more informed decisions. For recruitment, NASA analyzes data to understand which skills and traits lead to success in various roles. This helps refine their hiring process, ensuring they select candidates who are more likely to thrive.
In performance management, NASA gathers feedback from employees and managers to identify strengths and weaknesses within teams. This data-driven approach allows for targeted improvements, like additional training or team adjustments, to enhance performance.
For employee retention, NASA tracks engagement and satisfaction data to spot potential issues early. By addressing these concerns proactively, they improve employee satisfaction and reduce turnover.
Overall, NASA’s use of People Analytics helps streamline HR processes, making them more effective and responsive to employee needs and organizational goals.
Key Metrics for Skills-Based Talent Management
In the era of skills-based talent management, tracking the right metrics is essential for building a future-ready workforce. These metrics go beyond traditional HR measures to focus on identifying, developing, and leveraging employee skills as the foundation for organizational success.
By analyzing key skills-related metrics, HR leaders can gain actionable insights into workforce capabilities, bridge skills gaps, and align talent strategies with business goals.
Skills Utilization Rate
What It Is: Skills utilization rate measures the extent to which employees’ skills are being used effectively in their current roles.
Why It Matters: Underutilized skills can lead to disengagement and reduced productivity, while overutilization might indicate burnout risks. Understanding how employees’ skills align with their roles helps maximize their contributions and satisfaction.
How to Use It: Analyze skills data to identify employees whose skills are underutilized. Reassign them to roles or projects where their capabilities add the most value, improving engagement and performance.
Formula: Skills Utilization Rate = (Skills Used in Role / Total Skills of Employee) × 100
Skills Gap Rate
What It Is: Skills gap rate identifies the difference between the skills employees currently possess and those required to perform optimally or meet future demands.
Why It Matters: A high skills gap rate can impact productivity, innovation, and organizational agility. Tracking it allows HR teams to implement targeted upskilling and reskilling programs to bridge these gaps.
How to Use It: Use skills assessments to identify gaps on an individual, team, or organizational level. Prioritize training programs to address critical skill shortages and measure progress over time.
Formula: Skills Gap Rate = (Skills Required – Skills Possessed) / Skills Required × 100
Skills Development Completion Rate
What It Is: This metric tracks the percentage of employees who complete skills-based training or development programs.
Why It Matters: Tracking completion rates ensures that employees actively participate in learning initiatives that improve their skills. Low completion rates may signal issues like misaligned training content or lack of engagement.
How to Use It: Monitor program completion rates to assess participation and identify roadblocks. Align learning programs with employees’ career goals and organizational priorities to improve engagement and outcomes.
Formula: Skills Development Completion Rate = (Number of Employees Who Completed Training / Number Enrolled) × 100
Internal Skills Mobility Rate
What It Is: Internal skills mobility rate measures the percentage of employees who advance internally through promotions, lateral moves, or project-based roles by leveraging their skills.
Why It Matters: A high internal skills mobility rate demonstrates a strong culture of career development and skills growth. It reduces turnover, cuts external hiring costs, and fosters employee engagement.
How to Use It: Track how frequently employees move to new roles or projects based on their skills. If the rate is low, consider improving skills visibility, mentorship programs, or career pathing initiatives.
Formula: Internal Skills Mobility Rate = (Number of Internal Role Moves Based on Skills / Total Role Moves) × 100
Skills Proficiency Progress Rate
What It Is: This metric measures the improvement in employee skills over a defined period, tracked through skills assessments or learning outcomes.
Why It Matters: Improving skills proficiency ensures employees remain competitive, agile, and equipped to meet evolving job requirements. It also demonstrates the ROI of upskilling initiatives.
How to Use It: Regularly assess employees’ skills to track progress over time. Use this data to refine learning programs, personalize development plans, and demonstrate the impact of training initiatives on skills growth.
Formula: Skills Proficiency Progress Rate = (Skills Score After Training – Skills Score Before Training) / Skills Score Before Training × 100
Skills Alignment Index
What It Is: Skills alignment index evaluates the match between employees’ skills and the skills required for their current roles or future opportunities.
Why It Matters: Misalignment of skills and roles can hinder performance and lead to disengagement. Tracking this metric helps ensure employees are in roles where their skills add the greatest value.
How to Use It: Analyze skills alignment data to identify employees whose skills don’t match their current roles. Offer reskilling opportunities or reassign them to better-fit roles where their capabilities are fully leveraged.
Formula: Skills Alignment Index = (Skills Matched / Skills Required for Role) × 100
Learning and Development ROI
What It Is: L&D ROI measures the impact of skills-based learning programs on employee performance, productivity, and organizational outcomes.
Why It Matters: Investing in skills development is only valuable if it drives measurable outcomes. Tracking ROI ensures training efforts align with strategic goals and deliver tangible results.
How to Use It: Link training outcomes to improvements in productivity, skills proficiency, and business KPIs. Use this data to justify investments in learning programs and refine strategies for maximum impact.
Formula: L&D ROI = (Performance Gains from Training – Training Costs) / Training Costs × 100
Skills-Based Productivity Rate
What It Is: This metric measures how effectively employees’ skills contribute to achieving specific business outcomes or productivity goals.
Why It Matters: Tracking skills-based productivity helps organizations understand which skills are driving success and where gaps may hinder performance.
How to Use It: Link skills data to business outcomes, such as project completion rates, revenue per employee, or customer satisfaction scores. Use these insights to prioritize critical skills and optimize workforce performance.
Formula: Skills-Based Productivity Rate = (Business Output Linked to Skills / Total Skills in Use)
Using Skills-Based Metrics to Drive Change
Skills-based metrics are not just numbers—they are powerful tools for building an agile, skilled, and engaged workforce. By tracking and analyzing these metrics, HR leaders can:
- Identify and close critical skills gaps.
- Enable continuous learning and internal mobility.
- Align employee skills with organizational goals.
- Improve workforce productivity and agility.
The key is not just to collect skills data but to interpret it and act on it. For instance, if you observe a widening skills gap, implement targeted upskilling programs. If internal mobility rates are low, enhance career pathways to showcase opportunities for growth.
With the right skills-based HR metrics, organizations can transform workforce management into a strategic advantage, ensuring employees remain engaged, productive, and ready for the future.
How to Get Started with HR Analytics for Skills-Driven Talent Management
Implementing HR Analytics for skills-driven talent management is a strategic process. By following a structured approach, organizations can leverage data to optimize workforce capabilities and drive growth.
Step 1: Identify Skill-Based Metrics
Begin by identifying the skill-related metrics most critical to your organization’s success. Align these metrics with your business objectives to ensure they’re actionable. For example, if your organization aims to close skill gaps, focus on metrics such as skill proficiency levels, training completion rates, and internal mobility trends.
Consider additional areas like emerging skill demands, competency mapping, and upskilling effectiveness. Defining these metrics will enable you to gather targeted, relevant data.
Step 2: Choose the Right Tools for Skill Tracking
Selecting the right tools is essential for managing skill data effectively. Look for systems that can track skills across roles, teams, and the entire organization. Advanced talent management platforms with built-in skill assessments, gap analysis, and training recommendations are particularly useful.
For smaller organizations, simpler tools with customizable dashboards might suffice. Larger companies may benefit from comprehensive systems that integrate HR analytics with learning management systems (LMS) and workforce planning tools.
Step 3: Build a Skill Data Collection Framework
With tools in place, establish a framework for collecting skill-related data. This may include gathering information from employee skill assessments, training feedback, certifications, and performance reviews. Use this data to create skill profiles for employees and map these to job requirements.
Ensure consistency in your data collection methods to maintain accuracy. Automating data updates—such as syncing skill data from learning platforms—can streamline the process and minimize errors.
Step 4: Upskill Your HR and Talent Teams
To maximize the impact of HR Analytics in skills-driven talent management, ensure your HR teams have the necessary expertise. Provide training on topics such as skills taxonomies, data visualization, and predictive analytics for workforce planning.
Engage with specialists in learning and development (L&D) or external consultants who can help interpret complex data and design effective upskilling strategies. Equipping your team with these skills ensures they can translate data insights into actionable talent initiatives.
Step 5: Start with Targeted Skill Initiatives
Avoid attempting to tackle all skill challenges at once. Begin with focused initiatives, such as identifying critical skill shortages in a key department or evaluating the success of a recent upskilling program. Analyze the data to assess effectiveness, refine strategies, and measure outcomes.
Once you’ve demonstrated success in one area, expand your efforts by scaling skill-based analytics across other functions or teams. This iterative approach minimizes risks while building confidence in the use of HR Analytics.
By starting small and scaling strategically, organizations can unlock the full potential of HR Analytics in driving a skills-focused workforce strategy. This ensures a more agile and future-ready organization while aligning employee development with business goals.
Challenges in Implementing HR Analytics
Adopting HR Analytics offers great potential, but it comes with challenges that organizations need to address. Let’s look at some common hurdles and how to overcome them:
Data Quality and Integration
Reliable data is the foundation of HR Analytics. Inconsistent, outdated, or incomplete data can lead to flawed insights. If your data is scattered across different systems, it can be difficult to gain a clear view of your workforce.
Solution: Invest in data cleaning and integration. Standardize data entry processes and use software that connects different HR systems to ensure accurate, consistent data across the board.
Lack of Expertise
Many organizations still struggle to fully leverage People Analytics. In fact, a significant 39% of organizations report poor or very poor results in designing and implementing processes to extract value from People Analytics. This suggests a gap in expertise or experience that prevents companies from fully utilizing their data.
Solution: Organizations should consider hiring professionals with experience from other companies of similar size that have successfully implemented analytics. These experts can help build a stronger data strategy and provide the necessary skills to drive meaningful insights from HR data.
Privacy and Ethics
Employee data is sensitive. If employees feel their data is misused or not kept secure, it can erode trust and lead to legal issues. Privacy concerns are a significant challenge, especially with the growing focus on data protection laws.
Solution: Be transparent about data collection and use. Clearly communicate privacy policies and ensure compliance with regulations. Protect employee data by ensuring that only necessary personnel have access.
Skill Gaps
According to a PwC CEO survey, 77% of CEOs believe the biggest threat to their business is the lack of availability of key skills. This challenge extends to HR teams as well, where many professionals lack the technical expertise needed to analyze data effectively. Without these skills, it can be difficult to interpret data and apply the insights in meaningful ways.
Solution: Offer training in data analysis and analytics tools. HR teams should gain basic data skills to understand and use the insights effectively. For more complex needs, consider hiring data experts to complement the HR team.
Tools and Technologies in HR Analytics
The right tools are crucial for effectively implementing HR analytics. They help HR teams collect data, analyze insights, and make data-driven decisions. Among the various platforms available, Nestor stands out for its AI-powered features designed to improve talent management and employee engagement.
Nestor: AI-Powered Talent Management
Nestor is a platform that integrates talent management with analytics, making it easier for HR teams to manage skills, performance, and employee development. Its main focus is helping companies identify skill gaps, improve workforce planning, and align individual growth with company objectives.
Key Features of Nestor
Nestor offers a dynamic skills library that helps HR teams track and manage over 20,000 skills across industries. This makes it easier to understand the skills landscape within the organization and align employee capabilities with company needs.
Skills Assessment and Gap Analysis:
The platform provides tools to assess employee skills through self-assessments, peer feedback, and manager reviews. Using AI, it identifies skill gaps, helping HR teams plan upskilling and training initiatives effectively.
Based on the skill gaps identified, Nestor suggests tailored learning and development paths, aligning employee growth with the company’s goals and boosting engagement.
Performance Management:
Nestor links skills data directly to performance reviews, creating a more accurate and data-driven evaluation process. This helps HR leaders make objective decisions about promotions, development, and employee support.
Why Choose Nestor for HR Analytics?
Nestor is designed to help HR teams make more informed decisions about their workforce. The platform’s AI capabilities offer predictive insights and proactive recommendations, ensuring that HR efforts are focused on areas that matter most.
Additionally, Nestor’s user-friendly design makes it easy for HR teams to implement and manage, even for those new to talent management software. With customizable dashboards and reporting tools, it aligns perfectly with HR analytics goals: to use data to improve decision-making and employee outcomes.
In summary, Nestor is a powerful, AI-driven solution for HR analytics, helping companies align skills, performance, and development with organizational objectives. By offering insights into skills gaps, performance management, and personalized learning paths, it empowers HR leaders to create more engaged and productive teams.
Final Thoughts on HR Analytics
HR Analytics is a powerful tool that can transform your organization. It helps you make smarter decisions, improve performance, and address challenges before they escalate. By using data to guide your HR strategies, you move from reactive to proactive management.
The future of HR is data-driven. With HR Analytics, you can improve your workforce management and create a more productive, engaged, and satisfied team. The time to act is now. Start today and see the results for yourself.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About HR Analytics
What is HR Analytics?
HR Analytics is the process of collecting, analyzing, and applying workforce data to make informed decisions about hiring, performance, engagement, and retention. It helps HR teams move from intuition-based decisions to data-driven actions.
Is HR Analytics only for large organizations?
No, HR Analytics is beneficial for organizations of all sizes. Even small and mid-sized companies can use data to optimize their HR practices, improve recruitment, and enhance employee engagement.
How can HR Analytics improve employee retention?
HR Analytics helps identify patterns and factors contributing to employee turnover, such as job dissatisfaction, lack of growth opportunities, or poor management. By addressing these issues with targeted strategies, companies can improve employee satisfaction and reduce turnover rates.
What types of data should be collected for HR Analytics?
Key data to collect includes employee demographics, performance reviews, attendance records, compensation, training history, and turnover rates. Collecting this data allows HR teams to analyze trends and make informed decisions about talent management and organizational development.
What HR metrics should I track for analytics?
Key HR metrics to track include turnover rates, employee engagement scores, absenteeism, time-to-hire, cost-per-hire, employee productivity, and training effectiveness. These metrics provide insights into workforce health, recruitment efficiency, and employee satisfaction, all of which are critical for effective HR management.










